Contents
1. About LSVF
2. Architecture
3. Creation and Live Synchronization of RDB_RDF Views with LSVF
4. Creation and Incremental Maintenance of Linked Data Application Views
5. CASE STUDY: LinkedBrainz Live Tool
There is a vast content of structured data available on the Web of Data as Linked Open Data (LOD). In fact, a large number of LOD datasets are RDF views defined on top of relational databases, called RDB-RDF views. The content of an RDB-RDF view can be materialized to improve query performance and data availability. However, to be useful, a materialized RDB-RDF view must be continuously maintained to reflect dynamic source updates.
Furthermore, Linked Data applications, that consume data RDB-RDF view, can fully or partially replicate the contents of a materialized RDB-RDF view, by creating RDF application views defined over the RDB-RDF view. The generation of RDF application views improves the efficiency of applications that consume data from the LOD, and increases the flexibility of sharing information. However, the generation of RDF application views raises synchronization problems, since the original datasets can be continuously updated. Thus, updates on an RDB-RDF view must be propagated to maintain the RDF application views.
The LSVF framework is based on rules and procedures, that provides live synchronization of RDB_RDF views.
In the proposed framework (see Figure 1), rules are responsible for computing and publish the changeset required for the RDB-RDF view to stay in synchronization with the relational database. The computed changesets are used for incremental maintenance of RDB-RDF views and linked data application views.
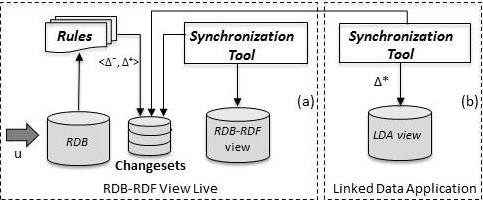
3. Creation and Live Synchronization of RDB_RDF Views with LSVF
Steps for creation and maintenance of Live RDB_RDB views using the LSVF framework:
- Define the RDB_RDF view ontology.
- Define the Mapping between the relational database schema and the RDB_RDF ontology.
- Create the triggers required to compute and publish the changesets.
- Materialize the RDB_RDF view using the mappings created in Step 2. An SPARQL end point is created for the RDB_RDF view.
- Initialize the changeset files.
- Configure the synchronization tool to propagate changesets to the RDB_RDF View.
4. Creation and Incremental Maintenance of Linked Data Application Views
Steps for creation and maintenance of application view defined over a Live RDB_RDB view:
- Define the application view ontology. The vocabulary of the application view on-tology must be a subset of the RDB_RDF view ontology vocabulary. Therefore the mappings for the application view can be automatically generated from RDB_RDF view mappings.
- Materialize the Application view using the mappings created in Step 1.
- Configure the synchronization tool to propagate relevant changesets to the application View.
5. CASE STUDY: LinkedBrainz Live Tool
MusicBrainz is an open music encyclopedia that collects music metadata and makes it available to the public. The MusicBrainz database is built on the PostgreSQL relational database engine and contains all of MusicBrainz music metadata.
The LinkedMusicBrainz View (LMB view) is intended to help
MusicBrainz to publish its database as Linked Data. The MusicBrainz Database is constantly updated. Hence, data stored in the LinkedMusicBrainz View can quickly become outdated. The LinkedBrainz Live tool (LBL tool) enables a continuous synchronization between LinkedMusicBrainz View and MusicBrainz relational database. The LBL tool was implemented using the LSVF Framework (Framework for Live Synchronization of RDF Views of Relational Data).
(For more information http://www.arida.ufc.br/livesynrdbrdf/linkedbrainzlive.html)
Important Links
SPARQL-endpoints for LMB View: http://virtuoso.mooo.com/sparql.
Changesets Publishe by LinkedBrainz Live tool: http:virtuoso.mooo.com/files/changesets/.
Dumps for LMB View: http://virtuoso.mooo.com/files/dumps/.
Synchronization Tool (Keep a RDF application view of LMB View in sync): https://github.com/narcisoarruda/LBL-Syncronization-tool.